Description
Introduction
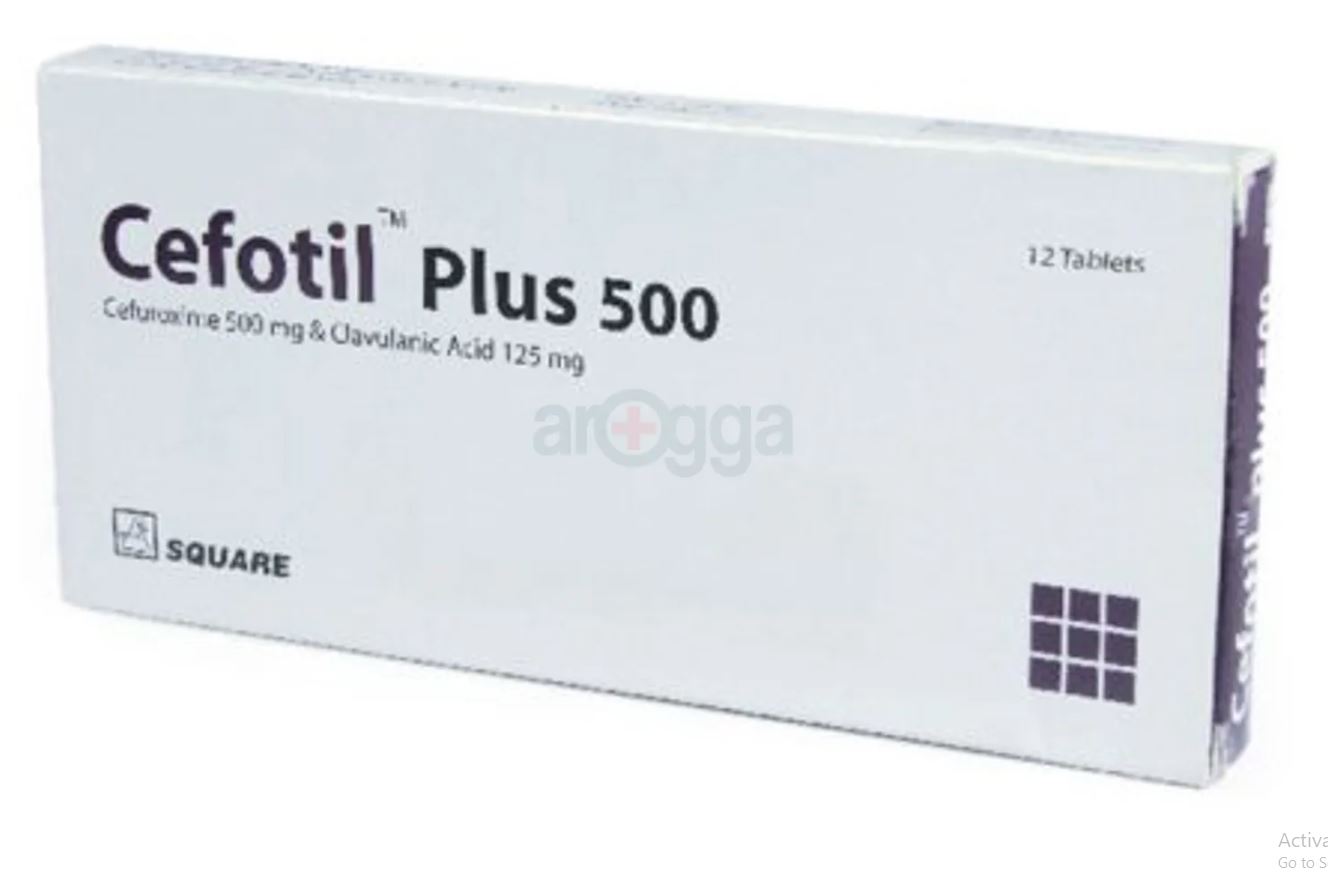
Cefotil Plus 500 is a combination medicine that is used to treat various types of bacterial infections. It fights against the microorganisms to prevent their growth and further spread of the infection. Cefotil Plus 500 is a prescription medicine. It is advised to take it as per the prescription. It can be taken with or without food, but it must be taken at a fixed time to ensure better efficacy. Do not consume more than the recommended dose, as this may have harmful effects on your body. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. The course of the treatment must be completed even if you feel better. Sudden discontinuation of the treatment may affect the potency of the medicine. Some common side effects of this medicine are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, indigestion, etc. If any of the side effects get aggravated, you must consult your doctor immediately. If you experience any allergic reaction (rashes, itching, swelling, shortness of breath, etc.), you must seek immediate medical help. Before taking this medicine, you should tell your doctor if you are taking any medicines for any health condition. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult with their doctor before taking it. Avoid drinking alcohol as it can cause excessive drowsiness with this medicine. It usually does not impair your ability to drive, but you should not drive if it makes you feel sleepy or dizzy. You must take adequate rest for a faster recovery, also take a healthy diet and drink plenty of water. Your doctor may ask for a few laboratory and diagnostic tests to know the effects of the medicine on your body.
Uses of Cefakind-CV Tablet
- Bacterial infections
Side effects of Cefakind-CV Tablet
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Increased liver enzymes
- Allergic reaction
How to use Cefakind-CV Tablet
Take this medicine in the dose and duration as advised by your doctor. Swallow it as a whole. Do not chew, crush or break it. Cefotil Plus 500 may be taken with or without food, but it is better to take it at a fixed time.
How Cefakind-CV Tablet works
Cefotil Plus 500 is a combination of two medicines: Cefuroxime and Clavulanic Acid. Cefuroxime is an antibiotic. It works by preventing the formation of the bacterial protective covering which is essential for the survival of bacteria in the human body. Clavulanic Acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor which blocks the action of enzymes produced by bacteria to inactivate Cefuroxime. Addition of Clavulanic Acid reduces resistance and enhances the activity of Cefuroxime against bacteria.
 Quick Tips
Quick Tips- You have been prescribed this combination medicine to treat bacterial infections, even if they have developed resistance.
- Do not skip any doses and finish the full course of treatment even if you feel better. Stopping it early may make the infection to come back and harder to treat.
- Take it with food to avoid an upset stomach.
- Diarrhea may occur as a side effect. Taking probiotics may help. Talk to your doctor if you notice bloody stools or develop abdominal cramps.
- Stop taking Cefotil Plus 500 and inform your doctor immediately if you develop an itchy rash, swelling of the face, throat or tongue or breathing difficulties while taking it.
- Do not use leftover medicine for treating any infection in the future. Always consult your doctor before taking any antibiotic.
 Brief Description
Brief DescriptionIndication
Pharyngitis, Acute otitis media, Lyme disease, Susceptible infections, Sinusitis,Otitis media, Skin and skin structure infections,Tonsillitis, Respiratory tract infections, Acute Maxillary Sinusitis, MDR Typhoid fever, Urinary tract infections, Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, Surgical Prophylaxis
Administration
Tab: May be taken with or without food. Oral susp: Should be taken with food.
Adult Dose
Adolescents & adults: Pharyngitis or Tonsillitis: 250 mg twice daily 5-10 days Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis: 250 mg twice daily 10 days Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis: 250-500 mg twice daily 10 days Secondary bacterial infections of acute bronchitis: 250-500 mg twice daily 5-10 days Community acquired pneumonia: 250-500 mg twice daily 5-10 days Uncomplicated skin & skin-structure infections: 250-500 mg twice daily 10 days MDR Typhoid fever: 500 mg twice daily 10-14 days Uncomplicated urinary tract infection: 250 mg twice daily 7-10 days Uncomplicated gonorrhea: 1000 mg single dose Lyme disease: 500 mg twice daily 20 days
Child Dose
Paediatric patients (3 months to 12 years) Pharyngitis or Tonsillitis: 20 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 5-10 days Acute otitis media: 30 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 10 days Acute bacterial maxillary sinusitis: 30 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 10 days Community acquired pneumonia: 30 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 5-10 days MDR Typhoid fever: 30 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 10-14 days Uncomplicated skin & skin-structure infections: 30 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 10 days Uncomplicated urinary tract infection: 20 mg/kg/day in two divided doses 7-10 days
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins.
Mode of Action
Cefuroxime binds to one or more of the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) which inhibits the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell wall, thus inhibiting biosynthesis and arresting cell wall assembly resulting in bacterial cell death. Addition of clavulanate inhibits beta-lactamase-producing bacteria; Clavulanic acid has a high affinity for and binds to certain ?-lactamases that generally inactivate Cefuroxime by hydrolyzing its ?-lactam ring. Combining clavulanate potassium with Cefuroxime extends the antibacterial spectrum of Cefuroxime to include many bacteria normally resistant to Cefuroxime and other penicillins and cephalosporins.
Precaution
Severe renal impairment; pregnancy, lactation; hypersensitivity to penicillins. Lactation: Drug excreted in breast milk; use with caution
Side Effect
>10% Diarrhea (4-11%; depends on duration) 1-10% Decreased hemoglobin or hematocrit (10%),Eosinophilia (7%),Nausea or vomiting (3-7%),Vaginitis (<5%),Transient rise in hepatic transaminases (2-4%),Diaper rash (3%),Increase in alkaline phosphatase (2%),Thrombophlebitis (2%),Increase in lactate dehydrogenase (1%) <1% Anemia,Cholestasis,Colitis,Dyspnea,Epidermal necrolysis,Increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine,Jaundice,Nephritis,Prolonged prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR),Rash,Stevens-Johnson syndrome,Stomach cramps,Transient neutropenia and leukopenia,Urticaria Potentially Fatal: Anaphylaxis, nephrotoxicity, pseudomembranous colitis.
Interaction
May enhance the nephrotoxic effect of strong-acting diuretics (e.g. furosemide) and aminoglycosides. May enhance the effect of oral anticoagulants. May reduce the efficacy of OCs. Probenecid prolongs the excretion of cefuroxime and elevated peak serum level.





There are no reviews yet.